Pose-based EKF SLAM on a Kobuki Turtlebot2
Hands-On Localization
Collaborator(s): Lisa Paul, Fatima Yousif
Overview
This project focuses on the implementation of Pose-Based SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping) using an Extended Kalman Filter (EKF) on a Kobuki Turtlebot. The PEKF SLAM (Pose-Based Extended Kalman Filter SLAM) algorithm tackles the core challenge of SLAM: simultaneously creating a map of an unknown environment while determining the robot’s position within that map. To assess the algorithm’s performance, testing was carried out in both simulated and real-world environments, demonstrating the feasibility and efficiency of the system.
Methodology
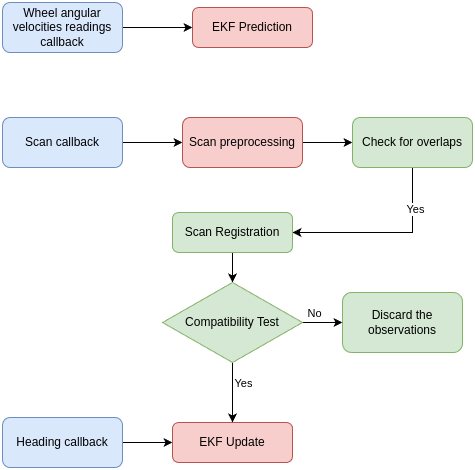
The PEKF SLAM algorithm integrates the following components for effective localization and mapping:
- Input Displacement Model: This model estimates the robot’s motion based on input commands.
- Heading Measurements: These measurements, taken from the Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU), improve the robot’s orientation estimation.
- 2D LiDAR Scan Displacement Observations: Iterative Closest Point (ICP) algorithms are used for scan matching, registering LiDAR scan displacements.
- ICNN Compatibility Test: Ensures that the observed scan displacements are statistically consistent with the expected displacement within a specified confidence level, enhancing robustness.
- View Poses: The positions where the environmental scans are captured are integrated into the state vector as view poses, enhancing the alignment of sensor data with the robot’s estimated position. This approach improves the accuracy of both localization and mapping by ensuring better fusion of the scan data with the robot’s trajectory.
The PEKF SLAM algorithm was tested in both simulated environments using the Stonefish simulator and real-world environments using a Kobuki Turtlebot platform equipped with a 2D LiDAR and IMU. These extensive tests provided insights into the algorithm’s performance across various scenarios.
Results
The results from both simulated and real-world tests showed that PEKF SLAM offers superior performance compared to conventional EKF approaches. The combination of sensor fusion techniques, including ICP for scan registration and ICNN compatibility testing, led to more accurate localization and mapping.
- Pose-Based EKF SLAM Algorithm: By integrating view poses into the state vector, the algorithm significantly improved the accuracy of localization and mapping.
- ICP Scan Registration: The use of ICP provided robust and precise registration of 2D LiDAR scan displacements, contributing to more accurate map creation.
- ICNN for Robustness: The ICNN compatibility test enhanced the system’s ability to handle noisy or inconsistent data, ensuring that scan displacements align with expected motion predictions.
The video below showcases the performance of the PEKF SLAM algorithm in a real-world environment, illustrating the robot’s ability to localize and map unknown surroundings efficiently.